Anúncios
Financial crime continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, making automated AML and KYC solutions essential for modern businesses seeking to protect themselves while maintaining operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
🔍 Understanding the Foundation: What AML and KYC Really Mean
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) represent two interconnected pillars of financial compliance that have transformed from optional best practices into mandatory requirements across global jurisdictions. AML encompasses the comprehensive framework of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income. KYC, meanwhile, focuses specifically on verifying customer identities and understanding their financial behaviors to assess potential risks.
Anúncios
These compliance frameworks have become increasingly complex as regulatory bodies worldwide tighten their oversight. Financial institutions, fintech companies, cryptocurrency exchanges, and even traditional businesses now face substantial penalties for non-compliance, ranging from hefty fines to criminal prosecution and reputational damage that can permanently destroy brand trust.
The traditional manual approach to AML and KYC compliance has proven inadequate in today’s fast-paced digital economy. Organizations processing hundreds or thousands of transactions daily simply cannot rely on human reviewers to catch every suspicious activity or verify every customer detail with the thoroughness and speed required by modern regulations.
Anúncios
💼 The Business Case for Automation in Compliance
Automation in AML and KYC processes delivers transformative benefits that extend far beyond simple cost savings. Organizations implementing automated compliance solutions typically experience a dramatic reduction in processing times, with customer onboarding that once took days or weeks now completed in minutes or hours.
The financial implications are substantial. Manual compliance processes require significant human resources, with specialized compliance officers commanding premium salaries. A single compliance team member might cost an organization between $60,000 and $120,000 annually, depending on experience and location. Multiply this across teams of ten or twenty professionals, and the costs become staggering.
Beyond direct labor costs, manual processes introduce error rates that automation dramatically reduces. Studies indicate that human reviewers miss approximately 5-15% of suspicious activities during manual reviews, while automated systems with machine learning capabilities can achieve detection rates exceeding 95%. This improved accuracy translates directly into reduced regulatory risk and fewer false positives that waste investigative resources.
Measurable ROI from Compliance Automation
Organizations implementing comprehensive AML and KYC automation typically observe return on investment within 12-18 months. The savings accumulate through multiple channels: reduced staffing requirements, faster customer onboarding leading to improved conversion rates, decreased regulatory penalties, and enhanced ability to scale operations without proportional increases in compliance costs.
Customer experience improvements represent another crucial benefit. Modern consumers expect instant gratification and seamless digital experiences. Automated KYC processes that verify identities in real-time meet these expectations while maintaining rigorous compliance standards, resulting in higher completion rates during onboarding and improved customer satisfaction scores.
🤖 Core Technologies Powering AML and KYC Automation
Several cutting-edge technologies work in concert to enable effective compliance automation. Understanding these foundational elements helps organizations make informed decisions when selecting or building automated compliance systems.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML algorithms form the intelligence layer of modern compliance systems. These technologies excel at pattern recognition, learning from historical data to identify suspicious behaviors that might indicate money laundering, fraud, or other financial crimes. Unlike rule-based systems that only catch known patterns, machine learning models continuously evolve, detecting novel schemes that criminals develop to evade detection.
Natural Language Processing (NLP), a subset of AI, enables systems to analyze unstructured data sources including news articles, social media posts, and legal documents. This capability proves invaluable for screening customers against sanctions lists and identifying politically exposed persons (PEPs) who require enhanced due diligence.
Optical Character Recognition and Document Verification
OCR technology enables automated extraction of information from identity documents, transforming images of passports, driver’s licenses, and utility bills into structured data that systems can validate instantly. Modern OCR solutions incorporate anti-spoofing features that detect fraudulent documents, including sophisticated forgeries that might fool human reviewers.
Advanced document verification goes beyond simple OCR, analyzing security features like holograms, microprinting, and UV-reactive elements. Biometric verification adds another security layer, using facial recognition to confirm that the person presenting documents matches the photographs on those documents.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology
Blockchain technology offers unique advantages for compliance processes, particularly in creating immutable audit trails and enabling secure information sharing between institutions. Some innovative solutions leverage blockchain to create decentralized KYC utilities where customers verify their identities once, with multiple institutions accessing this verified information while maintaining privacy and data security.
📊 Key Components of an Automated AML and KYC System
Effective automation requires integration of multiple functional components working together seamlessly. Understanding these building blocks helps organizations evaluate potential solutions comprehensively.
Customer Identity Verification
The identity verification component forms the entry point of the compliance process. Automated systems collect and verify customer information through multiple channels including document uploads, database checks, and biometric verification. The system cross-references submitted information against authoritative data sources, flagging inconsistencies automatically.
Risk-based authentication adjusts verification stringency based on customer profiles and transaction patterns. Low-risk customers might complete streamlined verification, while high-risk profiles trigger enhanced due diligence procedures automatically.
Transaction Monitoring and Screening
Continuous transaction monitoring analyzes customer activities in real-time, applying sophisticated algorithms to detect patterns indicative of money laundering or other financial crimes. The system establishes baseline behaviors for each customer, triggering alerts when activities deviate significantly from established patterns.
Screening functions automatically check customers and transactions against sanctions lists, PEP databases, and adverse media sources. These checks occur not just during onboarding but continuously throughout the customer relationship, ensuring that organizations respond promptly when customer risk profiles change.
Case Management and Reporting
When the system identifies potential issues, automated case management workflows route alerts to appropriate investigators with all relevant information compiled automatically. The system tracks investigation progress, ensures timely resolution, and maintains comprehensive documentation for regulatory reporting.
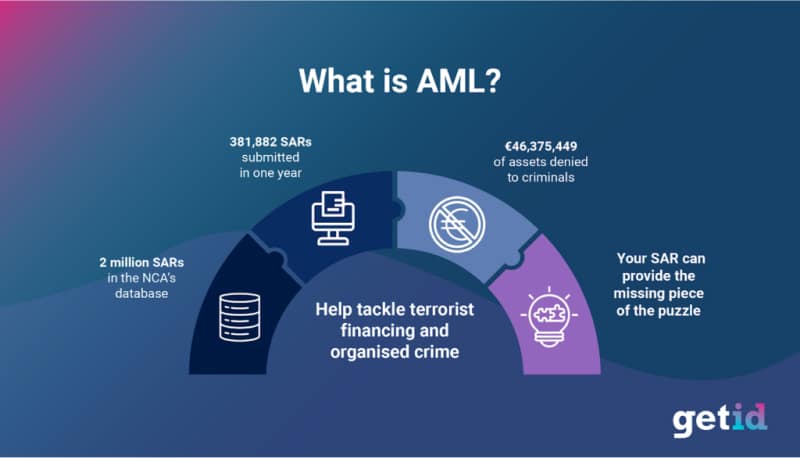
Automated reporting generates Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) and other regulatory filings, dramatically reducing the time compliance teams spend on administrative tasks. The system maintains complete audit trails, documenting every decision and action for regulatory examination.
🎯 Implementing AML and KYC Automation: A Strategic Approach
Successful implementation requires careful planning and execution across multiple dimensions. Organizations that approach automation strategically achieve better outcomes than those pursuing quick-fix solutions.
Assessing Current State and Defining Requirements
Begin by comprehensively documenting existing compliance processes, identifying pain points, bottlenecks, and areas where manual processes create unacceptable risks or costs. Engage stakeholders across compliance, operations, technology, and business units to understand requirements from multiple perspectives.
Regulatory requirements vary significantly across jurisdictions and industries. Map the specific regulations applicable to your organization, ensuring that any automated solution addresses all relevant compliance obligations. Consider future regulatory trends and select solutions with flexibility to adapt as requirements evolve.
Selecting the Right Technology Partner
The market offers numerous AML and KYC automation solutions, ranging from comprehensive enterprise platforms to specialized point solutions. Evaluate vendors based on technical capabilities, regulatory expertise, implementation support, and long-term viability.
Request demonstrations using your actual use cases rather than generic scenarios. Assess how solutions handle edge cases and complex situations that frequently occur in your business. Investigate the vendor’s update cadence and how they incorporate new regulatory requirements and emerging threats.
Integration with Existing Systems
Automated compliance solutions must integrate seamlessly with existing customer relationship management systems, core banking platforms, payment processors, and other business systems. Evaluate integration capabilities thoroughly, considering both technical feasibility and the effort required for implementation.
API-first architectures typically offer the most flexibility, enabling organizations to incorporate compliance checks into existing workflows rather than forcing customers and employees into entirely new processes. Modern microservices-based solutions provide better scalability and resilience than monolithic legacy systems.
⚖️ Balancing Automation with Human Oversight
Despite remarkable advances in automation technology, human judgment remains essential for effective compliance programs. The most successful implementations combine automated efficiency with human expertise in a complementary relationship.
Automated systems excel at processing vast quantities of data, identifying patterns, and flagging potential issues for review. However, complex cases requiring contextual understanding, nuanced judgment, or evaluation of ambiguous information still benefit from human analysis. The optimal approach deploys automation to handle routine tasks and preliminary analysis while directing human attention to situations where human capabilities provide the greatest value.
Organizations should establish clear escalation protocols defining when automated systems refer cases to human reviewers. These protocols should consider factors including risk severity, complexity, potential false positive rates, and regulatory requirements for human oversight in specific situations.
Training and Change Management
Implementing automation transforms compliance roles rather than eliminating them. Compliance professionals evolve from spending most time on data entry and routine checks to focusing on analysis, investigation, and strategic risk management. This transition requires thoughtful change management and comprehensive training programs.
Employees need training not just on operating new systems but on understanding how automated tools work, interpreting their outputs, and recognizing situations where automated recommendations require human judgment. Investing in this training ensures that organizations maximize the value of their automation investments while maintaining strong compliance cultures.
🚀 Advanced Capabilities: The Future of Compliance Automation
The compliance automation landscape continues evolving rapidly as new technologies mature and regulatory expectations advance. Organizations planning long-term strategies should consider emerging capabilities that will define next-generation compliance systems.
Predictive Risk Analytics
Advanced analytics move beyond detecting known patterns to predicting future risks based on subtle indicators. Machine learning models analyze thousands of variables to calculate risk scores that anticipate which customers or transactions present elevated risks before suspicious activities occur. This predictive capability enables proactive risk management rather than purely reactive detection.
Network Analysis and Entity Resolution
Sophisticated criminals often structure money laundering schemes across multiple accounts, institutions, and jurisdictions to evade detection. Network analysis capabilities map relationships between entities, identifying hidden connections that simple transaction monitoring might miss. Entity resolution technologies recognize when different records actually refer to the same individual or organization despite variations in how information is recorded.
Continuous Adaptive Learning
Next-generation systems incorporate feedback loops enabling continuous learning and improvement. When investigators review alerts, their decisions train the system to refine its detection algorithms. Over time, these systems become increasingly accurate for each organization’s specific risk profile, reducing false positives while maintaining high detection rates.
🔐 Addressing Privacy and Data Protection Concerns
Automated compliance systems necessarily collect and process sensitive personal information, creating significant privacy and data protection obligations. Organizations must balance compliance requirements with privacy regulations including GDPR, CCPA, and similar frameworks worldwide.
Implement privacy-by-design principles, collecting only information necessary for compliance purposes and retaining data no longer than required by regulatory obligations. Employ strong encryption for data in transit and at rest, and implement strict access controls ensuring that only authorized personnel can view sensitive information.
Transparency with customers about how their information is used for compliance purposes builds trust and satisfies regulatory disclosure requirements. Provide clear privacy notices explaining data collection, processing, and sharing practices related to AML and KYC procedures.
📈 Measuring Success: KPIs for Compliance Automation
Organizations need clear metrics to evaluate whether automated compliance systems deliver expected benefits and identify areas requiring optimization. Establish baseline measurements before implementation to enable meaningful comparisons.
Key performance indicators should span multiple dimensions including operational efficiency, risk management effectiveness, and customer experience. Operational metrics might include average processing time per customer onboarding, cost per transaction monitored, and staff hours required for case resolution. Risk metrics could track detection rates, false positive ratios, and regulatory examination findings.
Customer experience metrics such as onboarding completion rates, time to account activation, and customer satisfaction scores provide crucial insights into whether automation improves or hinders the customer journey. The most effective systems enhance both compliance effectiveness and customer experience simultaneously rather than achieving one at the expense of the other.
💡 Practical Steps to Begin Your Automation Journey
Organizations at any stage of compliance maturity can benefit from automation, but the starting point and approach should match current capabilities and resources. Small organizations might begin with point solutions addressing specific pain points, while larger enterprises might implement comprehensive platforms.
Start with thorough process documentation to understand current workflows, identify bottlenecks, and establish baseline metrics. Engage stakeholders early, building consensus around objectives and success criteria. Consider pilot programs that automate specific processes before expanding to comprehensive implementation, enabling learning and adjustment with limited risk.
Allocate sufficient resources not just for technology acquisition but for integration, testing, training, and ongoing optimization. Budget for change management activities that help employees embrace new ways of working. Plan for iteration, recognizing that optimization continues well beyond initial implementation.
🌐 Navigating Global Regulatory Complexity
Organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions face the challenging task of satisfying diverse and sometimes conflicting regulatory requirements. Automated systems can help manage this complexity by incorporating jurisdiction-specific rules and adapting processes based on customer location and transaction characteristics.
Leading compliance platforms maintain regulatory intelligence databases that automatically update as requirements change across different countries and regions. This capability proves invaluable for organizations expanding internationally, ensuring that compliance processes adapt automatically to new regulatory environments without requiring manual updates to every workflow.
Consider how Brexit, evolving cryptocurrency regulations, and emerging financial crime typologies create ongoing compliance challenges. Automation platforms that build flexibility into their architectures enable organizations to adapt quickly as the regulatory landscape shifts.
✨ Transforming Compliance from Cost Center to Competitive Advantage
Progressive organizations recognize that superior compliance capabilities create competitive differentiation rather than representing pure overhead. Automated compliance that enables faster, more reliable customer onboarding attracts customers who value smooth experiences. Strong compliance programs enhance reputation and enable partnerships with premium clients who conduct thorough due diligence on their business relationships.
Compliance automation generates valuable data and insights beyond satisfying regulatory obligations. Analysis of customer patterns, risk trends, and emerging threats informs strategic business decisions. Organizations leveraging these insights gain intelligence that drives product development, market expansion, and risk-adjusted pricing strategies.
The most successful implementations view compliance automation not as a technology project but as a business transformation initiative. By streamlining compliance processes, organizations free resources to focus on growth, innovation, and customer service while simultaneously reducing risks and satisfying regulatory obligations more effectively than ever before possible.
As financial crime grows more sophisticated and regulatory scrutiny intensifies, automated AML and KYC solutions transition from optional enhancements to essential infrastructure for any organization handling financial transactions. Those who embrace automation strategically position themselves for sustainable success in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
